1. Reynold's Number (Re)
The Reynolds number is the ratio of inertial force to viscous force.
- It is a dimensionless number.
- It is used to categorize the laminar and turbulent flow of fluids.
- It can be interpreted that when the viscous forces are dominant (slow flow, low Re) they are sufficient enough to keep all the fluid particles in line, then the flow is laminar.
- It is found that flow in a pipe, based on the diameter of the pipe if
But it should be pointed out that people have preserved laminar flow at very high Reynolds number through carefully monitored conditions.
- Even very low Re indicates viscous creeping motion, where inertia effects are negligible. When the inertial forces dominate over the viscous force (when the fluid is flowing faster and Re is larger) then the flow is turbulent.
2. Prandtl Number (Pr)
The Prandtl number is a dimensionless quantity that puts the viscosity of a fluid in correlation with the thermal conductivity.
- The Prandtl Number is a dimensionless number approximating the ratio of momentum diffusivity (kinematic viscosity) to thermal diffusivity.
- Remember that momentum diffusivity (kinematic viscosity) indicate the impulse transfer through molecular friction whereas thermal diffusivity indicates the heat energy transfer by conduction process.
- Prandtl Number provides a measure of the relative effectiveness of the momentum transported by diffusion.
- Fluids with small Prandtl numbers are free-flowing liquids with high thermal conductivity and are therefore a good choice for heat-conducting liquids.
- The Prandtl Number depends on the fluid properties.
3. Nusselt number
The Nusselt number is defined as the ratio of heat transfer by convection to the fluid to heat transfer by conduction under the same conditions.
- Convective heat transfer relationships are usually expressed in terms of Nusselt number as a function of Reynolds Number and Prandtl Number.
- We can also understand Nusselt Number like it is the ratio of conduction resistance offered by fluid if it were stable to the convection resistance offered by fluid. Remember it is always greater than one in case of fluids.
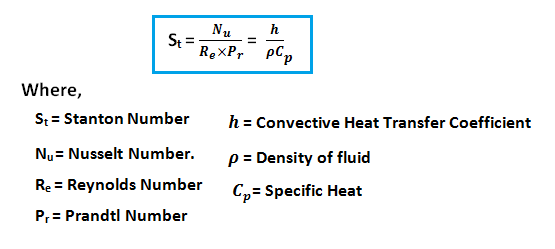
4. Stanton Number
It is the ratio of Nusselts Number to the product of Reynolds Number and Prandtl's Number.
- The Stanton Number (St), is a dimensionless number that measures the ratio of heat transferred into a fluid to the thermal capacity of the fluid.
5. Peclet number
Peclet number is the ratio of the heat flow rate by convection to the heat flow rate by conduction under a unit temperature gradient through a wall of thickness L.
- Peclet number is also written as the product of Reynold Number and Prandtl Number
6. Graetz Number
It is defined as the ratio of heat capacity of the fluid flowing through the pipe per unit length of pipe to the thermal conductivity of the pipe.- Graetz Number relates only for the heat flow to the fluid flowing through a circular pipe or tube.
7. Grashof Number
- It is used in natural convection or free convection.
Also Read
- What is Difference between Pressure and Stress ?
- What is Stress ?
- Necessity of Cooling Aeroplane At Higher Altitude While Temperature at Higher Altitude is Lower Than Ground ?
- Thermodynamic System and its types
- Automobile Lubrication System Classification
- Classification of Lubrication Oil Additive
- AutoCad Co-ordinate System
- SolidWork Commands List











Comments
Post a Comment